Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Overview of Blockchain
Indeed, Blockchain technologies changed the way we think about data. Actually, it is a kind of distributed digital ledger that maintains a record of transactions on various computers. Interesting is its immutability and transparency: a transaction, once recorded, cannot be altered-thereby building trust among participants.
Supply Chain and Logistics: Importance
Supply chains are actually the backbone of world commerce, with the purpose of making goods reach the final consumers efficiently and safely. The following are reasons why supply chains matter:
- Cost Efficiency: Streamlined operations reduce expenses. Timely Delivery: Customers expect their products on time.
- Risk Management: Efficiency in supply chains reduces risk causes because of delays or disruption. Integrating blockchain will overcome these issues, hence giving way to a much more transparent and dependable supply chain.
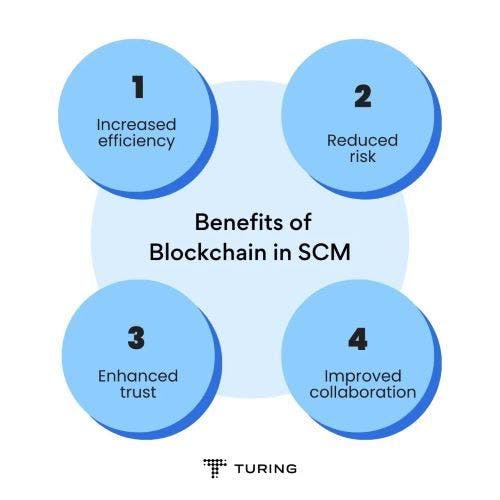
Advantages of Implementing Blockchain in Supply Chains
Transparency and Traceability
Probably the most salient benefit of blockchain in supply chains is that it offers transparency: it will record everything in a traceable manner, right from the manufacturer up to the consumer. With this traceability, whatever issue arises can be located.
Consider a food supplier who manages recalls more effectively by identifying contaminated batches quickly.
Improved Security Arrangements
Another critical advantage in security: blockchain utilizes a few forms of cryptography, and changes in data are indelible practically. A number of parties aslo verify the data before recording, adding to the security provided.
Data Integrity ensures only authorized users can change records.
Fraud prevention-less amount of counterfeit products, hence less supply lines. These will also enable the organization to operate better with advanced security because their information is well secured.

Streamlining Supply Chain Processes with Blockchain
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts also signify efficiency in the supply chain. In thee self-executing treaty, an action is done when set conditions are met. For example, take the case of a shipment. It gets released on arrival.
Reduced Delays: No waiting for anybody’s approval.
Less paperwork will reduce the operational cost, hence cost-effective.
It automates some workflows and makes the supply chain quicker and more reliable.
Real-time tracking of data with management
Other major advantages are real-time tracking. Due to this, blockchain enables immediately updated locations and statuses of products. As an example, a retailer can view shipments currently in transit to improve inventory management.
- Better Visibility: Stakeholders can account for assets at any given time.
- Data Accuracy: Less human error leads to better decision-making. With these tools, supply chains turn agile: quick to respond and absorb emergent changes and challenges.
Impact of Blockchain on Inventory Management
Reduction of Counterfeit Goods
Among the big influences that blockchain causes in inventory management, the reduction of counterfeit products can be counted. A business may be assured about the originality of the goods by means of a safe and tamper-proof record.
It allows luxury brands, for instance, to guarantee the authenticity of their products and thus increases customer confidence.
Brand Protection: Reduces fraud, saves reputation.
Consumer Trust: Building through transparency.
Efficient inventory tracking system
It also enhances inventory tracking systems, as business firms can track current levels of stock in real time to proactively manage replenishment.
Accurate Forecasting: Helps predict future inventory needs.
Reduced Waste: Reduces overstock and shortage, thus saving money. Inventory management will be easier and more effective with such innovative technologies being adopted, both for businesses and customers’ needs.
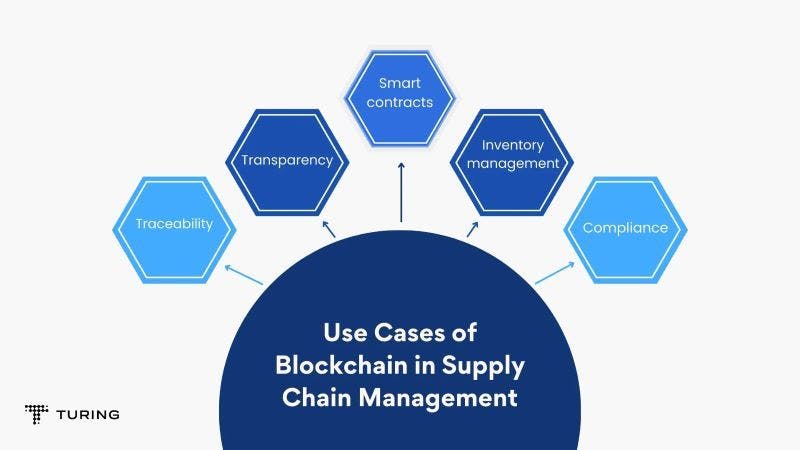
Blockchain Applications in Logistics
Supply Chain Financing
It involves supply chain financing where the blockchain creates some kind of transparency among the participants within the supply chains. It will make it easier for suppliers to get paid faster through this financing.
Imagine a small manufacturer instantly getting paid the moment a delivery is successfully made, due to predefined smart contracts.
- Liquidity Enhancement: Helps companies in handling cash flow management.
- Reduced risk: Lenders can verify transactions with ease to reduce defaulters.
Automated Documentation and Compliance
Blockchain also makes automated documentation and compliance easier. Companies like IBM’s Blockchain will have a more streamlined process by digitizing the records and ensuring that regulations are followed.
- Instant Access: Documents are accessible to stakeholders in a few mouse clicks.
- Audit Trails: Automatic records clearly show compliance history, which reduces fines or penalties.
Integrating these applications transforms logistics, making processes more efficient and reliable.
Enhancing Supplier Relationships through Blockchain
Improved Trust and Accountability
It raises the bar further in terms of trust and responsibility among suppliers since both parties can be aware of all the transactions and commitments transparently and indelibly.
For instance, a supplier can confidently share delivery timelines, knowing they’re documented securely.
Reduced disputes resulting from misunderstanding of records.
Mutual Liability: Parties are liable in regards to their engagements.
Increased efficiency in communicating with suppliers
Communication also becomes streamlined with blockchain. Instant access to the right data enables quick decision-making, reducing back-and-forth delays.
Centralized Information: All utilize the same updated information.
Faster resolutions: Issues can be addressed quickly, hence fostering better collaboration. The use of blockchain makes the companies to relate and connect well with the suppliers.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting Blockchain in Supply Chains
Integration with Existing Systems
Despite its advantages, adopting blockchain in supply chains brings challenges, especially integration with existing systems. Businesses often rely on legacy technologies that may not easily adapt well.
For example, if your warehouse management system isnt compatible with blockchain, it can create roadblocks.
- Cost Concerns: Upgrading systems can be expensive.
- Training Needs: Employes may require training to navigate new tools.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy Issues
Another hurdle is ensurings regulatory compliance and addressing data privacy. Blockchain’s transparency can conflict with datas protection law, particularly when sensitive information is involveded.
- Navigating Regulations: Different countries may have varying laws.
- Privacy Safeguards: Implementing measures to protect personal data is crucial.
By being aware of thes challenges, businesses can better prepare for a successful blockchain transition in their supply chains.