Introduction
Overview of Autonomous Vehicles
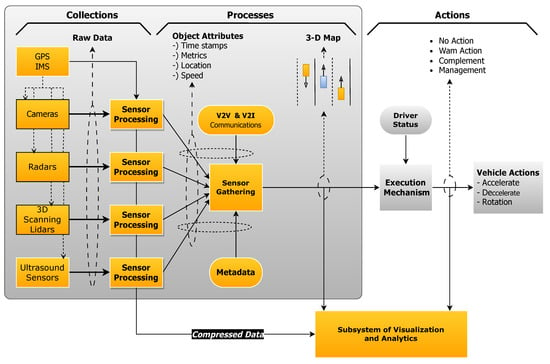
The power of the autonomous vehicle is really a paradigm shift in transportation. These are the vehicles that employ a suite of advanced integrated technologies, including sensors, cameras, GPS, and LiDAR, to navigate through complex environments without any help from humans. Think of a car talking fluently with the traffic light, recognizing pedestrians, and adjusting its speed in real time! A proper understanding in this respect gets pertinent with millions of such cars likely to flood our roads very soon.
Importance of Cybersecurity in Autonomous Vehicles
With increased innovation comes increased responsibility. Cybersecurity within autonomous vehicles will be highly important due to several compelling reasons:
- Personal Safety: A cyber breach would transform an AV into a weapon-a source of accidents.
- Data Privacy: These vehicles collect sensitive information, and their security should safeguard such data. Public Trust: Consumers have yet to earn confidence in AV security.
That’s what driving would be: powerful cybersecurity for our car, and our mind, on the road while forging ahead at this exciting time.
Vulnerabilities in Autonomous Vehicles
Threat of Hacking
Although autonomous vehicles are highly thrilling, they have a concern caused by complex software systems and the internet. A reason to worry that stems from this factor includes security threats such as hacking. To clarify, consider this robot vehicle for example; what will stop a bad program writer in his room thousands of miles away from getting into that vehicle and messing around with its control features, or causing a multiple car crash several miles away. The sad news is that the act of hacking cars from a distance is not a thing that can only be seen in movies but is a reality. This is due to the numerous opportunities many attacks present.
Focusing on the Risks
The possible outcomes of such cyber threats are staggering and especially:
1. Lack of Governance: Hackers might take charge steering, taking control of the vehicle’s brake and acceleration pedal mechanisms, thus endangering lives.
2. Privacy Infringement: Such unforeseen risks may result in breach of personal or confidential details of the people carried by the vehicles.
3. Traffics Accidents: The Car is taken to figures that are not existent Because what interrupts the state of equilibrium displacements and includes the manipulation of sensor information (position, velocity, angles etc.)
It is imperative that the problems at hand be tackled systematically for the development of future responsibilities on driverless cars.
Impact of Cybersecurity Breaches
Safety Warnings
This is the point that comes first when analyzing cyber risks of autonomous vehicles.. What happens if we read and understand it “Safety“? A compromised security system could bring about disastrous situations or occurrences:
Interference Concerns: The system being hacked may cause the vehicle to malfunction, causing accidents or even fatalities.
Anaegress Sensor Noises: In the event that sensor data has been manipulated, the vehicle perceives scenes wrongly and reacts unsuitably exposing itself to risks.
I swear each time my feet step inside the vehicle drives itself, I always pray it will make the best decision. Unfortunately it won’t be possible due to the presence of vulnerabilities.
Ethical or Legal Contexts
Aside from that, legal and ethical issues should be considered. They should be perceived as adequately covered by the legal system, should somebody get injured as a result of hacking the mechanism of the “self-driving” vehicle. Determining who bears responsibility in such situations is very difficult:
Question of Risks: The very assessment of guilt could become a hotly-contested legal issue.
Breach of Human Rights: Two, it is against the breach in data security that delves into sensitive use of data concerning individuals. They are also important issues in terms of business ethics.
That is why securing autonomous vehicles from cyber threats is more than a technical issue; it is also about saving lives and preserving people’s trust in the new modes of transportation available today.
Current Cybersecurity Measures
Encryption Technologies
The further ahead we advance into the autonomous vehicles world, to a greater extent we understand encryption technologies and the extent of application in their protection. With these technologies in place, it is impossible for sensitive data to get leaked to people who deserve no response. Image a situation where no one can access any information about your self, your autonomous vehicle transport, and even your cellular phone calls safely through encryption. This is the value of encryption:
Confidential Data: Encryption prevents outsiders from breaching security by converting data to unintelligible form.
Safe Communication: It secures data flow through which the data passed between the components of the vehicle including the interface with the other networks.
It feels good that I am at ease in the knowledge that my information is safe yet at the same time reluctance in giving up the ease of the tech advancements.
Intrusion Detection Systems
Besides encryption, there are also Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) that have a specific emphasis on the security of autonomous vehicles. After all, these measures are designed to detect and then report any unauthorized change in the status of the hardware.
Real-time Monitoring: IDS is able to find unusual activities before they propagate leading to appropriate responses.
Automated Responses: When danger is investigated, the machine can protect itself or even the part which is under attack will be secured.
However, it is worthwhile to look at these shouldering the intricacies of autonomous mechanisms because together these form the necessary defense – one that assures us that these vehicles are safe and sound while on road.
Collaboration for Cybersecurity in Autonomous Vehicles
Industrial Collaboration
Telecontrol of automotive systems is the order of the day: it involves the cooperation of many industrial frontlines for the multiple advantage of safety and security. As the experts argue, the association of industrial undertakings can be beneficial in different ways, including for enhancing cybersecurity. For every corporate body they share knowledge bases where each other they teach each other new experiences hence its perspectives and this is very risky in case of such threats so fully accepted well with satisfied industries. This is very risky in case of such threats so necessary measures have to be put in place. Industrial associates can do a pool collection of their resources and dedicate them to the R&D of security technologies in the automotive sector.
Joint Cooperation: How collaboration can help to cut costs on security technology research and development.
In my time, it is simply staggering to find out that such marriages can help touch every aspect of sociaty and they can change them completely.
State and Its Regulation
To further promote these partnerships, the enforcement of regulations plays a major role in enhancing cybersecurity within the automotive industry. On the one hand, far-reaching and awful as it might seem, numerous conventions in the form of ISO 21434 will be implemented to explain the notion of safety in an automotive world packed with driverless vehicles. The same is true with respect to any automobile featuring the above safety enhancements, i.e., there should be regulations in place that force compliance with the cyber security standards. Ensuring the development of new tasks, regulatory authorities also have the scope to change the existing levels of standards as time hangs and as such there are possible developments in the motor vehicle security.
In healing this loss of confidence with both the supply side and the demand side active in this endeavor, the industry plus the government will achieve the objective of making autonomous transportation more reliable and safer to use.
Future Challenges in Cybersecurity for Autonomous Vehicles
AI Integration
As we delve deeper into the realm of autonomous vehicles, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) comes with its own set of cybersecurity challenges. While AI enhances vehicle functionalities and decision-making, it also introduces vulnerabilities.
- Adversarial Attacks: Cyber attackers can exploit machine learning models, feeding them deceptive data to alter decision-making processes.
- Continuous Learning Needs: AI systems must constantly evolve, which makes them potentially susceptible to new threat vectors.
Personally, I’ve witnessed how essential it is for automotive companies to ensure robust defenses against these evolving threats to maintain public trust.
Connected Infrastructure
Moreover, the connected infrastructure surrounding autonomous vehicles amplifies security concerns. This interconnectedness allows for seamless communication between vehicles, traffic signals, and other entities.
- Attack Surfaces: Each communication channel becomes a potential entry point for cyberattacks, raising the stakes for system vulnerabilities.
- Standardization Needs: Without standardized security measures, the entire infrastructure could be at risk, making it imperative to establish regulations and frameworks governing these connections.
As we shape the future of transportation, proactive collaboration and stringent regulations will be pivotal in securing these advanced technologies.
Case Studies of Cybersecurity Incidents
Tesla
Tesla has faced several notable cybersecurity incidents that underscore the vulnerabilities present in autonomous vehicle technology. One significant breach occurred in 2020, when hackers attempted to deploy ransomware in a Tesla factory.
- Proactive Measures: Luckily, Tesla’s security systems detected the intrusion, allowing the company to thwart the attack before any data was compromised.
- Lessons Learned: This incident emphasizes the importance of rigorous cybersecurity protocols, such as continuous monitoring and anomaly detection, which are vital in safeguarding both production systems and vehicles on the road.
I remember the excitement—and the tension—around this case, as it highlighted how modern cybersecurity measures can make a difference.
Uber
Uber has also encountered serious cybersecurity challenges, particularly with its driverless technology. In 2016, hackers breached Uber’s systems and stole sensitive data from 57 million users, including driver license information.
- Data Exposure: The stolen data raised substantial privacy concerns, especially since the information could be used for fraudulent activities.
- Regulatory Ripple Effects: In response, Uber faced legal repercussions and stricter regulations, prompting the company to rethink its cybersecurity strategy and invest in safeguarding user data.
This incident serves as a powerful reminder of the consequences of lax cybersecurity in the tech-driven world of autonomous vehicles.
Strategies for Strengthening Cybersecurity
Continuous Testing
Ensuring the safety and security of autonomous vehicles requires processes of continuous testing. This means frequently checking the setups in place to see whether or not they can protect the systems from fresh cyber threats. Picture a team of engineers rehearsing and running simulations over and over again, preparing for every possible attack.
Key Attributes of Continuous Testing:
Penetration testing that finds where a system can be broken into.
Using resources available like software and hardware built for the car.
Bringing in an independent team to test for threats in the system to offer clarity beyond the old problems only appreciated in the presence of the people that developed such systems.
Incident Response Plans
Where does the aftermath lead to when disaster strikes? This is where incident response plans help significantly. An effective incident response plan provides precise guidance on managing a crisis.
Elements of a Successful Incident Response Plan:
A concise format for reporting a breach as well as response to the same.
Assignment of roles and responsibilities to team members.
Continued training keeping people’s attention on readiness, just as people are made aware of exits each time they travel on an airplane.
These tools are fundamental for every autonomous vehicle user to boost their confidence in the system and to prevent cyber threats. By front loading the effort in advance we are not improving the security but also the awareness that such an advanced technology will be in use.