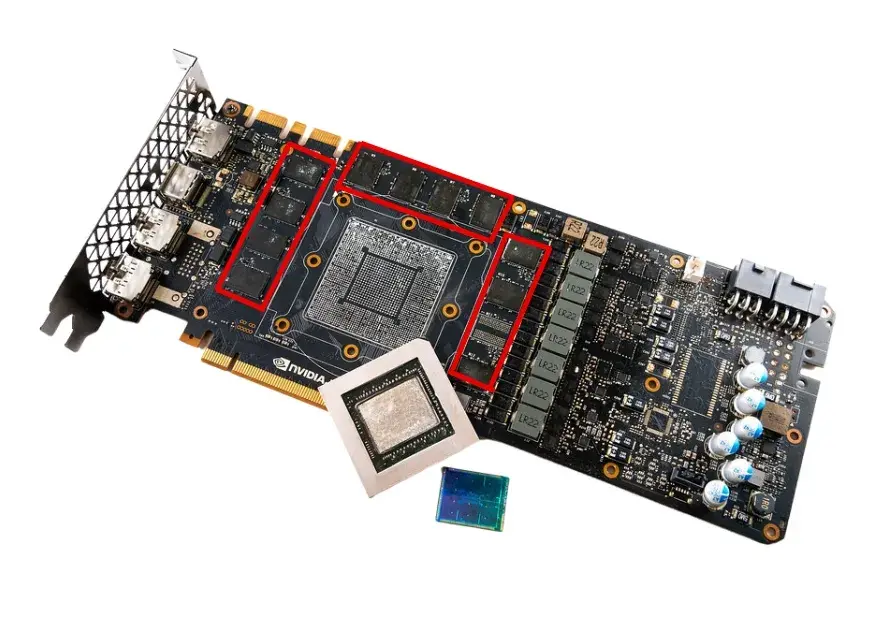
What is VRAM?
VRAM (Video RAM) is an example of RAM that has been structurally modified for saving image information for displays on computers. This is required to run complex graphic applications for video games or graphic design and ensure smooth texture rendering with 3D objects.
In general, it serves as a buffer between the computer’s main processor and its display. The image must be rendered by the main processor, which retrieves required data from system RAM and writes it into VRAM. After this, it transmits the data through interfaces like HDMI, DisplayPort, and for some earlier display types using VGA connectors, the video signal is converted digitally into analog form using RAMDAC, i.e., a RAM digital-to-analog converter.
Key VRAM Characteristics: Dual Porting
In the past, high-performance VRAM had dual-port architecture. This allowed simultaneous writing of new data onto the V-RAM while allowing the display to read the existing data at the same time. This ensures data flow to and from the memory. One of the biggest differences VRAM had with respect to the common system RAM was dual-port functionality. These differences were quite significant during the 1980s and 1990s.
Types of VRAM
Over a long period of years, there have been different types of VRAM emerging to satisfy varying performance needs. Here is the headway of these:
| Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Multibank DRAM (MDRAM) | Developed by MoSys, it divides memory into multiple 32 KB banks that can be accessed individually. | Improved performance due to concurrent access; cost-effective as VRAM can be tailored for specific resolutions. |
| Rambus DRAM (RDRAM) | A proprietary V-RAM developed by Rambus with a high-speed data transfer bus. | Enhanced data flow between the frame buffer and V-RAM. |
| Synchronous Graphics RAM (SGRAM) | A low-cost, single-ported RAM that mimics dual-port functionality by opening two memory pages simultaneously. | Efficient and affordable, often used in mid-range graphics solutions. |
| Window RAM (WRAM) | Dual-ported, high-performance V-RAM offering 25% more bandwidth than traditional V-RAM. | Ideal for high-resolution displays, supports true-color images up to 1600 x 1200 resolution. |
The most recent graphics card models have adopted GDDR6-individually utilize Graphics Double Data Rate 6-because it offers more capacity and width to its users than the former generation models like GDDR5. This advancement has popularized GDDR6 in the gaming PCs, playing consoles, and most HIPC systems.
GDDR6 has become the latest graphics memory used in graphics cards. It offers a much greater capacity and bandwidth compared with previous versions for example GDDR5. GDDR6 is popular in gaming PCs, game consoles, and a range of high-performance computing solutions.
VRAM Usage in Modern Applications
Gaming
You’re taught on data up to October 2023. The primary purpose of V-RAM in a game is to load time, quality of images, and resolution capability. The more images you get and textures you experience, the more V-RAM required. Here, it’s very particular about the requirements of each gaming activity defined according to its resolution.
| Resolution | Recommended VRAM |
|---|---|
| 720p | 2 GB |
| 1080p | 4 GB |
| 1440p (QHD) | 6-8 GB |
| 2160p (4K UHD) | 8-12 GB |
Video Editing
For high-resolution projects, more V-RAM has a tremendous effect on video editing as well.
| Video Resolution | Recommended VRAM |
|---|---|
| 720p-1080p | 8 GB |
| 4K | 16 GB |
| 8K (Professional Use) | 32-64 GB |
Tip: If you’re a professional editor working with 8K footage, investing in higher VRAM is critical to ensure smooth playback and rendering.
VRAM vs. System RAM
When we speak about RAM, it’s a general description that usually represents types of the memory. System RAM has its functions while V-RAM has a different function.
- System RAM: Uses general computing handles programs and the operating system.
- VRAM: Exclusively concentrates on processing and storing graphics-related data such that they show up on the visuals without any hitch.
Note: Modern GPUs often feature GDDR memory, which is specifically optimized for high-speed data transfer and rendering.
How to Check and Increase VRAM
Checking VRAM
To check how much VRAM your PC has on Windows:
- Open the search bar and type “Display Settings.”
- Select “Advanced Display Settings.”
- Click on “Display Adapter Properties.”
The amount of V-RAM will be listed under the properties tab.
You May Like: Your PC Specifications in Windows 11
Increasing VRAM
So, the easiest way to increase V-RAM is to move to a better graphics card. If this is not feasible, one can try these alternatives:
Adjust BIOS Settings:
- Access your BIOS by restarting your PC and pressing the designated key (usually F2, DEL, or ESC).
- Navigate to Graphics Settings or Advanced Chipset Features.
- Allocate more memory to the GPU (ranges vary from 128 MB to 512 MB).
Modify Registry Values (For Integrated Graphics):
- Open Registry Editor by typing
regeditin the Start Menu. - Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > Software > Intel. - Create a new DWORD (32-bit) value and name it.
- Set a value between 0 and 512.
- Restart your PC to apply changes.
Warning: Editing the registry incorrectly can cause system issues. Proceed with caution and back up your data beforehand.
History of VRAM
VRAM was invented in 1980 by researchers of IBM-Frederick Dill, Daniel Ling, and Richard Matick. This was patented in 1985 and commercially launched the following year as part of the ad-hoc adapter high resolution graphics for the RT PC system. Hence, dual port architecture of V-RAM has changed the graph processing paradigm towards more affordable and accessible high-resolution color display.